What are cord blood hematopoietic stem cells?
Cord blood hematopoietic stem cells are a group of primitive, highly undifferentiated cells that are the origin of all blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets) and immune cells. They are collected from the umbilical cord vein after the baby's umbilical cord is disconnected. No matching is required for autologous transplantation of babies. Transplantation from a genetically related family member has a high matching rate.
Clinical application scope of cord blood hematopoietic stem cells
According to the relevant national documents, the indications of cord blood hematopoietic stem cell therapy technology include
1. Hereditary and congenital diseases: bone marrow failure, hemoglobinopathies, severe immunodeficiency diseases, metabolic diseases.
2.Acquired diseases.
(1) Malignant diseases:acute leukemia, chronic leukemia, myelodysplastic syndromes, multiple myeloma, malignant lymphoma, and certain other malignancies.
(2) Non-malignant diseases: severe aplastic anemia, severe radiation sickness.
Since the success of Gluckman's first inter-sibling umbilical cord blood treatment for Fanconi anemia in 1988, umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation has been receiving increasing attention, and has become an effective alternative to allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, showing great potential.
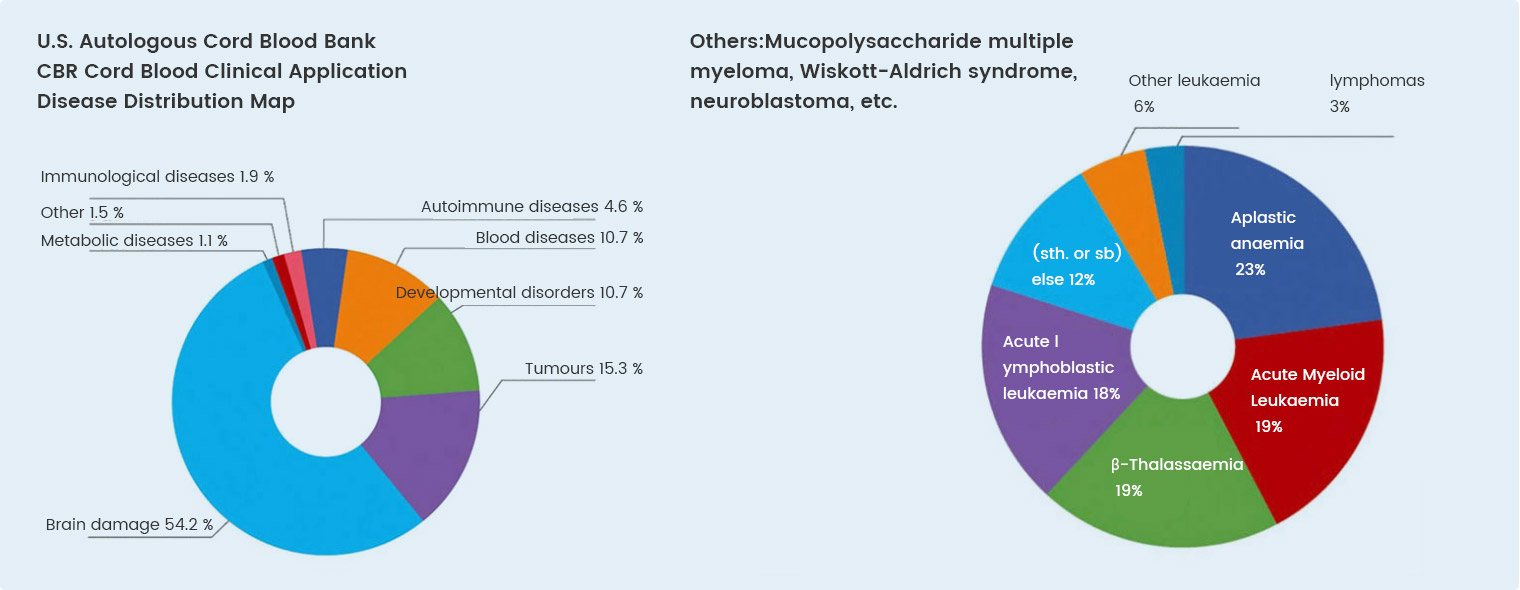
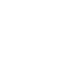
With the advancement of biotechnology, there are more than 1,000 registered studies on the clinical treatment of cord blood stem cells worldwide, involving more than 80 types of blood and non-blood diseases (lupus erythematosus, Crohn's disease, autism, cerebral palsy, spinal cord injury, etc.). There have been more than 40,000 cases of clinical application of umbilical cord blood in the world, among which, the total number of clinical applications of umbilical cord blood in China has exceeded 5,000 cases.
Advantages of cord blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Compared with unrelated bone marrow transplantation, cord blood transplantation has the following advantages:
1. The source of cord blood is abundant;
2. easy to collect, without any damage to the mother and fetus;
3. unlike unrelated bone marrow banking, cord blood is kept in physical form and will not be rejected by the donor;
4. the time required to search for HLA-compatible cord blood hematopoietic stem cells is short, allowing timely transplantation according to the patient's needs;
5. immature immune cells in cord blood, low incidence and mild severity of acute and chronic GVHD after transplantation, can tolerate large HLA differences, so cord blood banking requires fewer donors than bone marrow banking;
6. Less chance of various viral infections in cord blood, low incidence of post-transplant viral diseases

Significance of autologous storage of cord blood hematopoietic stem cells
The stored autologous cord blood hematopoietic stem cells can safeguard the health of the child and the family. In hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, autologous hematopoietic stem cells are 100% compatible, and the rate of full compatibility with siblings is more than 25%, and at least half compatible with parents, which is a great advantage compared with the allogeneic compatibility rate of 1 in 50,000~100,000. The chance of matching determines the chance of successful transplantation, so the storage of autologous placenta blood hematopoietic stem cells is actually an indispensable health guarantee for the child and all family members.